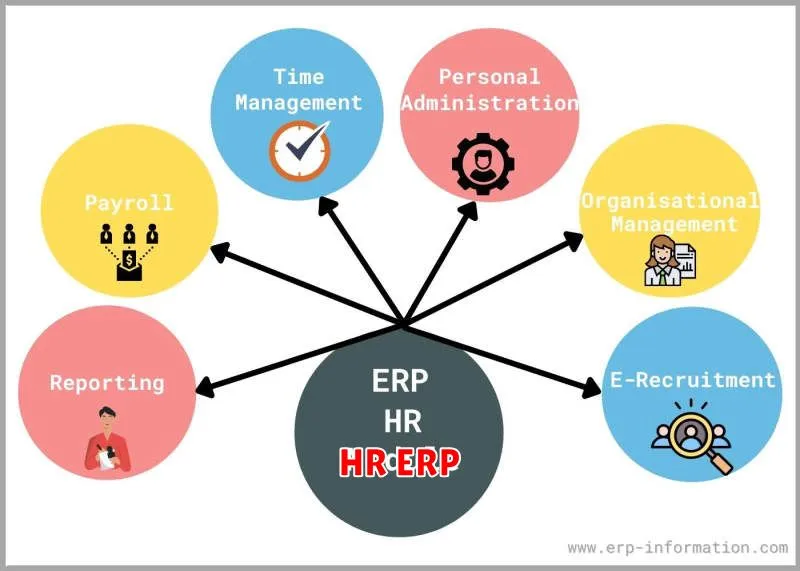
In today’s competitive business environment, effectively managing your human resources is paramount to success. With a growing number of employees and complex processes, organizations need a robust system to streamline HR operations and optimize talent management. This is where Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) comes in. ERP systems provide a centralized platform for managing all aspects of HR, from recruitment and onboarding to payroll and benefits administration. By leveraging the power of ERP software, businesses can achieve greater efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance employee engagement. This article will delve into the vital role of ERP in managing human resources effectively, exploring its key benefits and how it can empower organizations to make informed decisions about their workforce.
The Evolving Role of Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management (HRM) has undergone a significant transformation in recent years, evolving from a purely administrative function to a strategic partner in driving business success. This evolution has been fueled by several factors, including technological advancements, globalization, and the changing demographics of the workforce.
Traditionally, HRM focused on tasks such as recruitment, payroll, and employee relations. However, in today’s dynamic business environment, HRM professionals are expected to play a much broader role. They are now responsible for developing and implementing strategies that attract, retain, and motivate a talented workforce. This includes:
- Talent Acquisition: Proactively sourcing and attracting top talent by leveraging various channels and technologies.
- Employee Development: Investing in employee growth through training, mentorship, and career development programs.
- Performance Management: Setting clear goals, providing feedback, and recognizing employee contributions.
- Culture and Engagement: Fostering a positive work environment that promotes employee satisfaction and engagement.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Creating a workplace that values and embraces diversity, fostering a sense of belonging for all employees.
The rise of technology has significantly impacted HRM practices. Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) have automated many administrative tasks, freeing up HR professionals to focus on strategic initiatives. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are also being used to streamline recruitment, improve employee engagement, and analyze workforce data.
The changing demographics of the workforce also present new challenges and opportunities for HRM. The rise of Millennials and Gen Z, with their unique expectations and values, has prompted organizations to re-evaluate their employee benefits and workplace culture. The increasing diversity of the workforce also requires HRM professionals to be culturally sensitive and inclusive.
The evolving role of HRM is essential for organizations to thrive in the 21st century. By embracing technology, focusing on employee experience, and adapting to changing demographics, HRM can become a strategic asset that drives business success.
How ERP Supports Core HR Functions
Human Resource (HR) functions are essential for any organization, playing a critical role in attracting, managing, and retaining talent. Traditionally, HR processes were often fragmented and manual, leading to inefficiencies and challenges in managing employee data, payroll, benefits, and other critical areas. However, the advent of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems has revolutionized HR operations, providing a comprehensive platform to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and gain valuable insights into the workforce.
ERP systems offer numerous benefits for HR functions, including:
- Centralized Employee Data Management: ERP systems provide a centralized repository for all employee data, including personal information, employment history, payroll details, benefits, performance reviews, and training records. This consolidated view eliminates data silos and ensures consistency across different HR processes.
- Automated Payroll and Benefits Administration: ERP systems can automate payroll processing, including calculating salaries, deductions, and taxes. They can also streamline benefits administration, allowing employees to access and manage their benefits online.
- Streamlined Recruitment and Onboarding: ERP systems can help organizations manage the entire recruitment process, from job posting to candidate screening and onboarding. They provide tools for talent acquisition, background checks, and employee training.
- Performance Management and Development: ERP systems support performance management by providing tools for setting goals, conducting performance reviews, and tracking employee progress. They can also be used to identify training needs and facilitate employee development.
- Improved Compliance and Reporting: ERP systems help organizations comply with labor laws and regulations by providing tools for tracking employee time and attendance, managing leave requests, and generating compliance reports.
By integrating HR functions with other business processes, ERP systems enable organizations to gain a holistic view of their workforce and make informed decisions. The data gathered through ERP systems can be used to identify trends, analyze employee performance, and forecast workforce needs. This data-driven approach empowers HR professionals to proactively manage talent and optimize resource allocation.
In conclusion, ERP systems have become indispensable tools for modern HR departments. By automating processes, centralizing data, and providing valuable insights, ERP systems help organizations streamline HR operations, improve efficiency, and optimize workforce management. As technology continues to evolve, ERP systems will undoubtedly play an even more prominent role in shaping the future of HR.
Benefits of Using ERP for Human Capital Management
In today’s competitive business landscape, it’s crucial for organizations to effectively manage their most valuable asset: their human capital. Enterprises Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become indispensable for streamlining various business processes, and their application in Human Capital Management (HCM) has revolutionized how organizations manage their workforce.
Enhanced Efficiency and Automation
ERP systems for HCM automate numerous tasks, freeing up HR professionals to focus on strategic initiatives. From payroll processing and benefits administration to performance management and talent acquisition, ERP solutions streamline operations, reduce manual errors, and enhance overall efficiency.
Centralized Data and Improved Visibility
One of the key benefits of ERP for HCM is the consolidation of employee data into a centralized repository. This provides a comprehensive view of the workforce, enabling organizations to gain valuable insights into workforce demographics, skills, performance, and engagement. This data-driven approach empowers HR teams to make informed decisions and develop effective strategies.
Streamlined Talent Acquisition and Onboarding
ERP systems facilitate seamless talent acquisition and onboarding processes. They enable organizations to manage job postings, track candidates, and automate the hiring process. Moreover, ERP solutions simplify the onboarding process by providing new hires with access to essential information, benefits enrollment, and training resources.
Improved Performance Management and Development
ERP systems equip organizations with tools to effectively manage employee performance. They enable organizations to set goals, track progress, provide feedback, and conduct performance reviews. Furthermore, ERP solutions support employee development by providing access to training programs, mentorship opportunities, and career advancement pathways.
Compliance and Risk Mitigation
Staying compliant with labor laws and regulations is crucial for any organization. ERP systems for HCM help organizations ensure compliance by automating tasks like payroll calculations, benefits administration, and employee data management. They also help organizations manage risk by providing tools to track employee attendance, time off requests, and other relevant information.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
ERP systems provide organizations with a wealth of data about their workforce. This data can be used to analyze trends, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions about workforce planning, talent development, and compensation strategies.
Conclusion
Adopting ERP for Human Capital Management offers numerous benefits for organizations seeking to optimize their workforce management. By streamlining processes, centralizing data, and providing tools for performance management and development, ERP systems empower HR teams to make informed decisions and create a more engaged and productive workforce.
Talent Acquisition and Onboarding
Talent acquisition and onboarding are crucial aspects of any successful organization. They play a vital role in attracting, hiring, and integrating new employees into the company culture, ensuring a smooth transition and maximizing their potential.
Talent Acquisition
Talent acquisition is the process of finding, attracting, and hiring the best talent for an organization. It involves a series of steps, including:
- Defining the job requirements
- Identifying potential candidates through various channels
- Screening applications and conducting interviews
- Making hiring decisions and extending offers
Effective talent acquisition strategies focus on building a strong employer brand, utilizing diverse recruiting channels, and engaging with top candidates to create a positive candidate experience.
Onboarding
Onboarding is the process of welcoming and integrating new employees into the organization. It involves providing them with the necessary information, training, and support to help them succeed in their roles.
A comprehensive onboarding program should include:
- Orientation sessions to introduce the company culture, policies, and procedures
- Job-specific training to equip employees with the skills and knowledge required for their roles
- Mentorship and support from managers and colleagues
- Opportunities for networking and building relationships within the team
A successful onboarding process helps new employees feel welcomed, confident, and engaged, leading to increased productivity, retention, and job satisfaction.
Benefits of Effective Talent Acquisition and Onboarding
Investing in robust talent acquisition and onboarding practices offers numerous benefits, including:
- Attracting and retaining top talent
- Improving employee engagement and productivity
- Reducing employee turnover and hiring costs
- Enhancing company culture and values
- Boosting innovation and competitiveness
In today’s competitive job market, it is essential for organizations to prioritize talent acquisition and onboarding to ensure they have the right people in the right roles to achieve their strategic goals.
Performance Management and Training
Performance management is a crucial aspect of any organization’s success. It encompasses the processes and strategies that are used to ensure that employees are performing at their best and contributing effectively to the organization’s goals. Effective performance management systems involve setting clear performance expectations, providing regular feedback, offering opportunities for growth and development, and recognizing and rewarding achievements.
Training plays a vital role in enhancing employee performance. It equips employees with the necessary skills, knowledge, and competencies to excel in their roles. Effective training programs should be tailored to the specific needs of the organization and its employees, and they should be designed to be engaging, interactive, and relevant to the work being done.
The Link Between Performance Management and Training
Performance management and training are inextricably linked. Performance management provides a framework for identifying areas where employees need development, while training provides the tools and resources to address those needs. By integrating these two processes, organizations can create a culture of continuous improvement and growth.
Benefits of Effective Performance Management and Training
Organizations that invest in robust performance management and training programs reap numerous benefits, including:
- Improved employee performance and productivity
- Increased employee engagement and motivation
- Reduced turnover and absenteeism
- Enhanced organizational effectiveness and competitiveness
Key Components of a Successful Program
A successful performance management and training program should include the following key components:
- Clear performance expectations: Employees must have a clear understanding of what is expected of them.
- Regular feedback: Feedback should be provided on a regular basis, both positive and constructive.
- Opportunities for growth and development: Employees should be provided with opportunities to learn and develop new skills.
- Recognition and rewards: Employees should be recognized and rewarded for their achievements.
- Performance reviews: Performance reviews should be conducted regularly to assess progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Training programs: Training programs should be tailored to the specific needs of the organization and its employees.
Conclusion
Performance management and training are essential for any organization that wants to achieve success. By implementing effective programs, organizations can create a culture of high performance, continuous improvement, and employee engagement. It’s important to remember that these processes are ongoing and require constant attention and evaluation to ensure they remain relevant and effective.
Compensation and Benefits Administration
Compensation and benefits administration is a critical aspect of human resource management that involves managing employee compensation and benefits programs. It encompasses various tasks, including designing and implementing compensation structures, administering benefits plans, and ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
Compensation refers to the monetary and non-monetary rewards that employees receive in exchange for their work. This can include salary, wages, bonuses, commissions, and other forms of incentive pay. Benefits, on the other hand, are non-wage compensation provided to employees in addition to their salary. Common examples of benefits include health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and life insurance.
Effective compensation and benefits administration plays a crucial role in attracting, retaining, and motivating employees. It helps create a competitive and fair work environment that fosters employee satisfaction and productivity. By providing competitive pay and a comprehensive benefits package, organizations can attract and retain top talent, while also demonstrating their commitment to employee well-being.
Key responsibilities of compensation and benefits administration include:
- Conducting job evaluations to determine the value of different roles within the organization.
- Developing compensation structures that are aligned with market rates and internal equity.
- Administering payroll, ensuring accurate and timely payment of salaries and wages.
- Managing benefit plans, including enrollment, eligibility, and claims processing.
- Communicating compensation and benefits information to employees.
- Ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations, such as the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA).
The benefits of a well-managed compensation and benefits administration program include:
- Improved employee morale and motivation.
- Increased employee retention.
- Enhanced recruitment efforts.
- Reduced administrative costs.
- Stronger organizational performance.
In today’s competitive business landscape, compensation and benefits administration is more important than ever. By implementing effective strategies, organizations can create a rewarding work environment that attracts and retains talent, while also driving business success.
Employee Self-Service Portals
An employee self-service portal, or ESS portal, is a web-based platform that allows employees to access and manage their own HR-related information and processes. These portals provide a convenient and efficient way for employees to handle tasks such as:
- Viewing pay stubs and tax information
- Updating personal information (address, contact details, etc.)
- Requesting time off
- Enrolling in benefits
- Accessing company policies and procedures
- Submitting expense reports
ESS portals offer numerous benefits for both employees and employers:
Benefits for Employees
- Increased efficiency and convenience: Employees can access information and complete tasks 24/7, without having to wait for HR assistance or go to the office.
- Improved transparency: Employees have access to their own HR data and can see how their information is being used.
- Enhanced employee engagement: By giving employees control over their own HR processes, ESS portals can empower them and increase their sense of ownership.
Benefits for Employers
- Reduced administrative burden: ESS portals automate many HR tasks, freeing up HR staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Improved accuracy and efficiency: Automated processes reduce the risk of errors and increase the speed of HR transactions.
- Enhanced employee satisfaction: By providing employees with a convenient and user-friendly experience, ESS portals can boost employee morale and satisfaction.
- Cost savings: ESS portals can reduce administrative costs by eliminating paper processes and manual tasks.
Overall, employee self-service portals are a valuable tool for modern organizations. They help to improve efficiency, transparency, and employee engagement, while reducing administrative burden and costs.
Data Security and Compliance in HR ERP
In today’s digital age, organizations are increasingly reliant on Human Resource (HR) systems to manage their workforce effectively. HR Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, in particular, play a pivotal role in streamlining HR processes, from recruitment and onboarding to payroll and performance management. However, as these systems store vast amounts of sensitive employee data, data security and compliance become critical considerations.
Data security encompasses the measures taken to protect employee information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. Compliance refers to adhering to relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards that govern the handling of personal data.
Compliance with data privacy regulations is paramount for HR ERP systems. Organizations need to ensure their systems are compliant with laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, and other regional or national data protection laws.
Key data security and compliance considerations for HR ERP systems include:
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive employee data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Implementing strong access controls to limit access to employee data based on roles and responsibilities.
- Data Masking: Redacting or replacing sensitive information with non-sensitive data for testing and development purposes.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting periodic audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security policies.
- Employee Training: Educating employees on data security best practices to minimize the risk of data breaches.
Implementing robust data security and compliance measures in HR ERP systems is essential to protect employee privacy, maintain organizational reputation, and comply with legal obligations. By prioritizing these considerations, organizations can ensure the secure and ethical management of their workforce data.
Integrating ERP with Other HR Systems

In today’s dynamic business environment, organizations are increasingly adopting a holistic approach to managing their operations, leading to the integration of various systems to streamline processes and improve efficiency. One crucial integration is between Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and other Human Resources (HR) systems.
Traditionally, ERP and HR systems existed as separate entities, with limited communication and data sharing. This siloed approach resulted in fragmented data, inefficient workflows, and a lack of real-time insights. However, as businesses recognize the importance of a connected and integrated ecosystem, the need for seamless integration between these two systems has become paramount.
Benefits of ERP and HR System Integration
Integrating ERP and HR systems offers a multitude of benefits, including:
- Enhanced Data Accuracy: Eliminates data redundancy and inconsistencies by enabling data synchronization across systems.
- Improved Efficiency and Automation: Automates HR processes, such as payroll, benefits administration, and performance management, freeing up HR professionals to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Real-Time Insights: Provides access to comprehensive data, allowing organizations to make informed decisions based on real-time information.
- Enhanced Employee Experience: Streamlines employee onboarding, benefits enrollment, and other HR processes, creating a positive and efficient employee experience.
- Reduced Costs: Streamlines operations, eliminates manual tasks, and reduces administrative overhead.
Integration Approaches
Several approaches can be employed to integrate ERP and HR systems, including:
- Point-to-Point Integration: Direct connection between specific modules of the ERP and HR systems.
- Middleware Integration: Utilizes middleware software to facilitate communication and data exchange between the systems.
- Cloud-Based Integration: Leveraging cloud-based platforms for seamless integration and data synchronization.
Key Considerations for Integration
Before embarking on integration, organizations should consider:
- Business Requirements: Clearly define the business objectives and specific integration needs.
- Data Mapping: Ensure consistent data definitions and mapping between the two systems.
- Security: Address security concerns and ensure data privacy and integrity.
- Integration Tools and Technologies: Choose appropriate integration tools and technologies based on the complexity and scale of the integration.
Conclusion
Integrating ERP and HR systems is a strategic move for organizations seeking to optimize their operations and enhance employee experience. By leveraging the benefits of seamless data flow and automated processes, businesses can achieve greater efficiency, cost savings, and informed decision-making.
Case Studies of Successful HR ERP Implementations

Implementing a new HR ERP system can be a complex and challenging process, but when done correctly, it can significantly improve an organization’s human resources management capabilities. To understand how successful HR ERP implementations look, let’s delve into some case studies.
Case Study 1: Company XYZ
Company XYZ, a global manufacturing company, was struggling with fragmented HR processes and outdated systems. They decided to implement an HR ERP system to streamline operations and improve employee experience. They chose a cloud-based solution to ensure scalability and accessibility. During implementation, they involved key stakeholders from across the organization, including HR, IT, and business leaders, to ensure buy-in and smooth adoption. They also invested in comprehensive training for employees to familiarize them with the new system. The results were impressive. Company XYZ saw a significant reduction in manual processes, improved data accuracy, and enhanced employee engagement. They were able to make more data-driven decisions and improve overall HR efficiency.
Case Study 2: Company ABC
Company ABC, a retail organization with multiple locations, was facing challenges with payroll processing and talent management. They decided to implement an HR ERP system that offered integrated modules for payroll, talent acquisition, and performance management. The company implemented a phased approach, starting with payroll and then gradually rolling out other modules. They also prioritized data migration and integration to ensure seamless transition. As a result, Company ABC saw a significant reduction in payroll errors, improved talent acquisition processes, and enhanced performance management practices. The new system helped them better understand their workforce, optimize talent development, and improve overall HR efficiency.
Key Learnings from Successful Implementations
These case studies highlight several key learnings for organizations considering implementing an HR ERP system:
- Strong Leadership Support: Effective leadership engagement is crucial for successful implementation.
- Clear Goals and Objectives: Define clear objectives and desired outcomes from the implementation.
- Thorough Planning and Preparation: Plan meticulously, including system selection, data migration, and training.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involve key stakeholders from across the organization to ensure buy-in and collaboration.
- Change Management: Implement a comprehensive change management strategy to ensure smooth adoption.
- Continuous Improvement: Treat implementation as an ongoing process, continuously seeking ways to optimize the system and processes.
By following these key learnings, organizations can increase their chances of achieving a successful HR ERP implementation and realize the many benefits it offers.