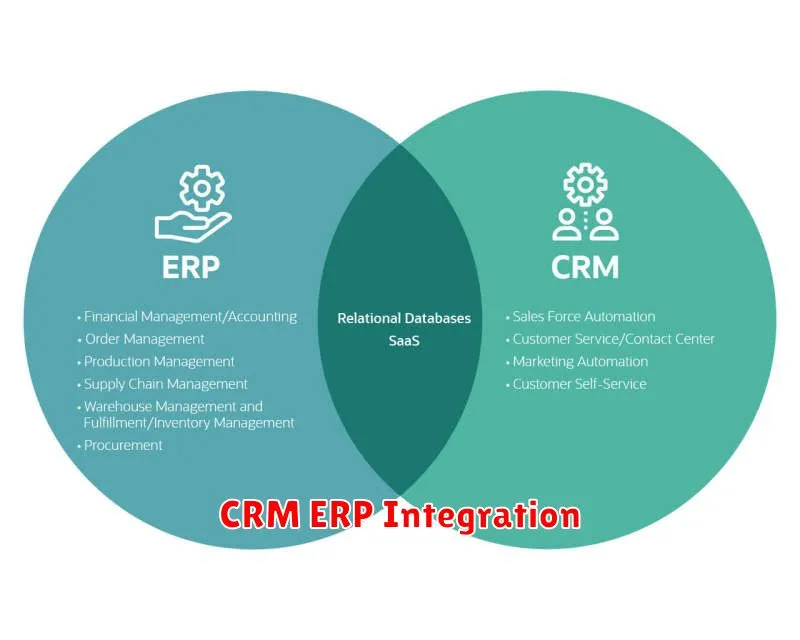
Are you struggling to manage your business operations efficiently? Are you tired of working with multiple systems and losing valuable time and data? Then it’s time to consider integrating your CRM with your ERP. By integrating these two vital systems, you can streamline your processes, gain valuable insights into your customers and operations, and ultimately boost your bottom line. This comprehensive guide will provide you with the essential information you need to understand the benefits of CRM-ERP integration and how to successfully implement it in your organization. Whether you’re a small business owner or a large enterprise, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to unlock the power of integration and transform your business operations.
Benefits of CRM and ERP Integration
Integrating your CRM and ERP systems can be a game-changer for your business. This powerful combination creates a unified platform that streamlines operations, improves data accuracy, and enhances customer experience. It eliminates silos and fosters seamless communication across departments, leading to increased efficiency and profitability.
One of the most significant benefits of CRM and ERP integration is improved customer insights. By combining customer data from both systems, you gain a comprehensive view of customer interactions and purchase history. This allows you to personalize marketing campaigns, offer tailored products and services, and provide exceptional customer service.
Another major advantage is enhanced operational efficiency. With integrated systems, you can automate processes like order fulfillment, inventory management, and billing, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors. This frees up your team to focus on more strategic tasks.
Improved decision-making is a key benefit of CRM and ERP integration. By having access to real-time data from both systems, you can make informed decisions about pricing, inventory levels, marketing strategies, and more. This data-driven approach helps you optimize your business operations and achieve better results.
Increased profitability is a direct consequence of these benefits. With improved efficiency, better customer insights, and enhanced decision-making, you can drive sales, reduce costs, and boost your bottom line.
While implementing CRM and ERP integration may require some initial investment, the long-term benefits far outweigh the costs. It is a strategic investment that can transform your business, leading to sustainable growth and success.
Choosing the Right Integration Approach
In the realm of software development, integration plays a crucial role in connecting different systems and applications to achieve seamless functionality. With numerous integration approaches available, selecting the most suitable one is paramount for ensuring successful project outcomes. This article delves into the key considerations and best practices for choosing the right integration approach.
Understanding Your Integration Needs
Before embarking on the integration journey, it’s imperative to have a clear understanding of your integration needs. Consider the following factors:
- Integration Scope: Determine the extent of integration, whether it involves a few applications or a complex ecosystem of systems.
- Data Volume and Frequency: Assess the volume and frequency of data exchanged between systems to choose an approach that can handle the workload efficiently.
- Real-Time vs. Batch Processing: Decide whether data needs to be integrated in real-time or can be processed in batches.
- Security Requirements: Ensure the chosen approach adheres to stringent security protocols to protect sensitive data.
Common Integration Approaches
There are various integration approaches to choose from, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
1. Point-to-Point Integration
This approach involves direct connections between individual applications. It’s simple to implement but can become complex and challenging to manage as the number of connections increases.
2. Enterprise Service Bus (ESB)
ESBs act as a central hub for message routing and transformation, simplifying integration between multiple systems. They offer flexibility and scalability but can be complex to configure and maintain.
3. API Integration
APIs provide a standardized interface for interacting with applications, enabling seamless data exchange and integration. This approach offers high flexibility and scalability but requires careful design and security considerations.
4. Message Queues
Message queues facilitate asynchronous communication between systems, allowing applications to send and receive messages without blocking each other. This approach is suitable for scenarios requiring high performance and loose coupling.
5. Cloud-Based Integration Platforms as a Service (iPaaS)
iPaaS solutions offer a cloud-based platform for managing and orchestrating integration processes. They provide pre-built connectors, automation tools, and scalability benefits. However, they may have vendor lock-in and cost implications.
Factors to Consider When Choosing
When selecting the most appropriate integration approach, consider the following factors:
- Complexity: Choose an approach that aligns with the complexity of your integration needs. Simple solutions may suffice for straightforward integrations, while complex approaches are needed for intricate scenarios.
- Scalability: Ensure the chosen approach can accommodate future growth in data volume, system connections, and functionality.
- Security: Prioritize security considerations and select an approach that meets your organization’s security requirements.
- Cost: Analyze the upfront and ongoing costs associated with each approach, including implementation, maintenance, and ongoing support.
- Time to Market: Consider the time required to implement and deploy the integration solution, balancing speed with quality.
Best Practices for Integration
To enhance integration success, adhere to these best practices:
- Define Clear Requirements: Thoroughly document the integration needs, including data mapping, business rules, and performance expectations.
- Implement Robust Testing: Conduct comprehensive testing to ensure data integrity, functionality, and performance.
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor the integration process to identify and address potential bottlenecks or performance issues.
- Embrace Agility: Foster a culture of continuous improvement and adapt to changing integration needs.
Conclusion
Choosing the right integration approach is a crucial step in achieving successful software integration. By carefully considering your integration needs, exploring available options, and following best practices, organizations can streamline processes, improve data flow, and unlock the full potential of their applications.
Data Mapping and Synchronization

Data mapping and synchronization are crucial processes for managing and integrating data across different systems and applications. They involve establishing relationships between data elements from multiple sources and ensuring that these elements are consistent and up-to-date.
Data Mapping
Data mapping defines the relationships between data elements in different systems. It involves identifying corresponding fields, attributes, and values across various data sources. For example, a customer name in one system might correspond to the “first name” and “last name” fields in another system. This mapping process is essential for accurate data transfer and integration.
Data Synchronization
Data synchronization ensures that data across different systems remains consistent and up-to-date. It involves automatically updating data in one system when changes occur in another. This can be achieved through various methods, including:
- Real-time synchronization: Data is updated immediately whenever changes are made in any system. This ensures continuous consistency but can be resource-intensive.
- Batch synchronization: Data is updated periodically, usually at scheduled intervals. This approach is less resource-intensive but may introduce a delay in data consistency.
- Change data capture (CDC): Tracks changes made to source data and applies them to target systems. This method offers a balance between efficiency and real-time updates.
Benefits of Data Mapping and Synchronization
Implementing effective data mapping and synchronization processes offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved data quality: Consistent data across systems ensures accuracy and reliability.
- Enhanced data integration: Seamless data flow between systems enables efficient data sharing and analysis.
- Increased efficiency: Automated data synchronization eliminates manual data updates, saving time and effort.
- Better decision-making: Accurate and up-to-date data supports informed business decisions.
Challenges and Considerations
While data mapping and synchronization provide numerous advantages, there are also potential challenges:
- Data complexity: Complex data structures and diverse data sources can make mapping and synchronization intricate.
- Data governance: Establishing clear data ownership and access control is crucial for data integrity and security.
- Performance impact: Real-time synchronization can impact system performance, requiring careful optimization.
Conclusion
Data mapping and synchronization are essential for effectively managing and integrating data across systems. By establishing clear relationships between data elements and ensuring consistent updates, organizations can enhance data quality, improve integration, and gain valuable insights for better decision-making. Careful planning, robust tools, and ongoing monitoring are crucial for successful implementation and ongoing maintenance.
Integration of Key Business Processes

Business process integration is the process of unifying different business processes into a single, cohesive system. This can be achieved through various means, such as technology, organizational restructuring, or a combination of both. The goal of process integration is to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
There are many benefits to integrating key business processes, including:
- Improved efficiency: By automating tasks and streamlining workflows, businesses can improve efficiency and reduce the time it takes to complete tasks.
- Reduced costs: Integration can help businesses save money by eliminating redundancies, reducing waste, and improving resource utilization.
- Enhanced customer satisfaction: By providing customers with a seamless experience, businesses can improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Increased agility: Businesses with integrated processes are better able to adapt to changing market conditions and customer needs.
There are several key considerations for integrating business processes:
- Identify the key processes: The first step is to identify the key processes that need to be integrated. This can be done by conducting a process mapping exercise.
- Choose the right technology: There are many different software solutions available for process integration. It is important to choose a solution that is right for the specific needs of the business.
- Develop a strong implementation plan: A well-defined implementation plan is essential for a successful process integration project. This plan should outline the scope of the project, the timeline, and the resources that will be required.
- Communicate effectively: It is important to communicate the benefits of process integration to all stakeholders, including employees, customers, and suppliers.
Integrating key business processes can be a complex undertaking, but the benefits are well worth the effort. By carefully planning and executing the process, businesses can achieve significant improvements in efficiency, cost savings, and customer satisfaction.
Real-time Data Sharing Between Systems
In the fast-paced world of modern technology, the ability to share data between systems in real-time is crucial for driving efficiency, improving decision-making, and staying ahead of the competition. Real-time data sharing enables organizations to access and process information as it occurs, eliminating delays and ensuring timely insights. This article explores the concept of real-time data sharing, its benefits, challenges, and common approaches used to achieve seamless data flow between systems.
Benefits of Real-time Data Sharing
Real-time data sharing offers numerous advantages for organizations across various industries:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Real-time data provides insights that can inform immediate actions, leading to more effective decision-making.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: By automating data exchange and eliminating manual processes, real-time data sharing streamlines operations and reduces bottlenecks.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Real-time insights into customer behavior and preferences enable organizations to deliver personalized experiences and responsive service.
- Faster Innovation: Real-time data facilitates experimentation and rapid prototyping, fostering innovation and product development.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations that can leverage real-time data gain a competitive edge by making faster and more informed decisions than their rivals.
Challenges of Real-time Data Sharing
While real-time data sharing offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges:
- Data Volume and Velocity: Handling large volumes of data streaming in real-time requires efficient infrastructure and data processing capabilities.
- Data Security and Privacy: Ensuring data security and compliance with privacy regulations is paramount when sharing sensitive information between systems.
- Data Consistency and Integrity: Maintaining data consistency and integrity across multiple systems is essential for accurate decision-making.
- System Integration Complexity: Integrating different systems and ensuring seamless data flow can be a complex and time-consuming process.
Approaches to Real-time Data Sharing
Various approaches can be used to achieve real-time data sharing between systems:
- Message Queues: Message queues act as intermediaries, allowing systems to exchange data asynchronously. Examples include Apache Kafka and RabbitMQ.
- Streaming APIs: Streaming APIs enable real-time data ingestion and processing. Examples include Twitter API and Google Cloud Pub/Sub.
- Change Data Capture (CDC): CDC technologies track changes in data sources and replicate them to target systems in real-time.
- Real-time Databases: Real-time databases are designed for high-volume data ingestion and processing, providing real-time updates. Examples include Apache Cassandra and MongoDB.
Conclusion
Real-time data sharing is a transformative technology that empowers organizations to leverage the power of real-time insights. By overcoming the challenges and adopting suitable approaches, businesses can unlock the full potential of real-time data, leading to enhanced decision-making, improved operational efficiency, and a competitive advantage in today’s dynamic environment.
Improving Customer Service and Satisfaction
In today’s competitive marketplace, providing exceptional customer service is no longer a “nice to have” – it’s a must-have. Happy customers are loyal customers, and they’re more likely to recommend your business to others. This translates to increased revenue, brand loyalty, and a stronger reputation.
Key Strategies for Enhanced Customer Service
Here are some key strategies to implement to elevate your customer service and drive satisfaction:
- Emphasize Proactive Communication: Don’t wait for customers to reach out with problems. Keep them informed about order status, potential delays, and other relevant updates.
- Provide Multiple Channels: Offer convenient communication channels like email, phone, live chat, and social media to ensure customers can reach you easily.
- Empower Your Team: Equip your staff with the knowledge, tools, and authority to resolve issues quickly and efficiently.
- Seek Feedback: Regularly solicit feedback from customers through surveys, reviews, and post-interaction follow-ups.
- Personalize the Experience: Utilize customer data to tailor interactions and provide personalized recommendations.
Benefits of Exceptional Customer Service
Investing in customer service isn’t just about boosting satisfaction – it yields tangible business benefits:
- Increased Sales: Happy customers are more likely to make repeat purchases.
- Reduced Customer Churn: Excellent service fosters loyalty and prevents customers from switching to competitors.
- Positive Word-of-Mouth: Satisfied customers are your best brand ambassadors.
- Enhanced Brand Reputation: Strong customer service builds trust and strengthens your brand image.
Conclusion
By prioritizing customer service and adopting these strategies, you can create a positive and lasting impact on your business. Remember, customer service is not just a department – it’s a philosophy that should permeate every aspect of your operations.
Monitoring and Measuring Integration Success

Integration is a crucial aspect of any business, whether it’s a merger, acquisition, or simply implementing a new system. It can be a complex process, involving multiple teams, systems, and data points. Successfully integrating these different elements can lead to significant benefits, such as increased efficiency, improved collaboration, and a more unified customer experience. However, without proper monitoring and measurement, it can be difficult to determine whether the integration is truly achieving its goals. This is where integration success metrics come into play.
These metrics provide a framework for tracking the progress of the integration and identifying areas that need attention. By carefully selecting and monitoring these metrics, organizations can ensure that their integration initiatives are delivering the desired outcomes. Here are some key areas to consider when defining integration success metrics:
- Technical Metrics: These metrics focus on the technical aspects of the integration, such as system performance, data quality, and uptime. They help assess the stability and reliability of the integrated systems.
- Business Metrics: These metrics measure the impact of the integration on key business objectives, such as revenue growth, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency. They help evaluate the overall value delivered by the integration.
- User Adoption Metrics: These metrics track the extent to which users are adopting the integrated systems and processes. They provide insights into the user experience and identify any barriers to adoption.
In addition to these categories, specific metrics can be tailored to the unique needs and goals of each integration project. Some examples of specific metrics include:
- Number of integration errors: This metric helps track the stability of the integration and identify any recurring issues that need to be addressed.
- Data synchronization rate: This metric measures the efficiency of data transfer between systems, ensuring that all data is accurate and up-to-date.
- Customer satisfaction score: This metric assesses the impact of the integration on customer experience, helping to ensure that the integration is meeting their needs.
- Time to value: This metric tracks how quickly the integration is delivering tangible benefits, such as increased revenue or reduced costs.
- Return on investment (ROI): This metric measures the financial impact of the integration, quantifying the return on the investment made in the integration project.
By carefully monitoring these metrics, organizations can gain valuable insights into the success of their integration efforts. This data can then be used to make informed decisions about future improvements, resource allocation, and overall integration strategy. It’s important to note that success metrics should be established before the integration process begins, allowing for proactive monitoring and adjustments throughout the project lifecycle.
Integration success metrics are essential tools for maximizing the benefits of any integration project. By carefully defining, tracking, and analyzing these metrics, organizations can ensure that their integration initiatives are delivering the desired outcomes, leading to a more efficient, collaborative, and successful business.