Deciding between an ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and an MRP (Material Requirements Planning) system can be a daunting task for manufacturing businesses. Both solutions offer valuable tools for managing operations, but they cater to different needs and priorities. This article will delve into the core differences between ERP and MRP, outlining their key features and functionalities. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each, you’ll be able to make an informed decision about which software is best suited for your specific manufacturing requirements, ultimately driving efficiency and profitability.
Understanding Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a production planning and inventory control system that utilizes computer software to manage and monitor the materials needed for manufacturing. It helps businesses determine the precise amount of raw materials, components, and finished products required to meet production demands. MRP is vital for companies across various industries, especially those with complex manufacturing processes and intricate supply chains.
Key Components of MRP
MRP systems typically encompass several core components, working in synergy to optimize production and inventory management:
- Bill of Materials (BOM): A comprehensive list detailing all the materials, components, and subassemblies needed to produce a finished product.
- Master Production Schedule (MPS): A schedule outlining the planned production quantities and delivery dates for finished products.
- Inventory Records: A database containing information on the current inventory levels for each material and component, including their location and status.
- Purchase Orders: Documents that outline the quantities and specifications of materials ordered from suppliers.
- Production Orders: Instructions for manufacturing specific products based on the MPS and BOM.
Benefits of Implementing MRP
Implementing an MRP system offers a plethora of benefits, streamlining production processes and enhancing operational efficiency. Here are some key advantages:
- Reduced Inventory Costs: MRP helps optimize inventory levels, minimizing storage costs and reducing the risk of stockouts.
- Improved Production Planning: MRP provides real-time visibility into material availability and production progress, facilitating better planning and scheduling.
- Enhanced Supply Chain Management: By managing supplier relationships and procurement processes, MRP strengthens the overall supply chain.
- Increased Productivity: With improved planning and inventory control, production processes can be more efficient, leading to increased productivity.
- Reduced Lead Times: MRP optimizes material flow, shortening production lead times and ensuring timely delivery of finished products.
Conclusion
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is an indispensable tool for companies seeking to optimize their production processes, manage inventory effectively, and enhance supply chain management. By implementing an MRP system, businesses can achieve significant benefits, including reduced inventory costs, improved planning, and increased productivity. This ultimately leads to a more streamlined, efficient, and profitable operation.
Understanding Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a business process management software that helps organizations manage day-to-day activities, such as finance, human resources, supply chain, manufacturing, and customer relationship management. ERP systems integrate all of these processes into a single system, providing a centralized view of the business.
ERP systems have become increasingly popular in recent years, as businesses look for ways to improve efficiency and streamline operations. They offer a number of benefits, including:
- Improved efficiency and productivity
- Reduced costs
- Enhanced decision-making
- Better customer service
- Increased compliance
ERP systems are typically implemented on a cloud-based platform, which allows businesses to access the software from anywhere with an internet connection. Cloud-based ERP systems are becoming increasingly popular due to their affordability, scalability, and ease of use.
Key Features of an ERP System
An ERP system typically includes a variety of modules that support different business functions. Some common modules include:
- Financial Management: This module helps businesses manage their finances, including accounts payable, accounts receivable, budgeting, and forecasting.
- Human Resource Management: This module helps businesses manage their workforce, including payroll, benefits, and employee performance.
- Supply Chain Management: This module helps businesses manage their supply chain, including procurement, inventory, and distribution.
- Manufacturing Management: This module helps businesses manage their manufacturing operations, including production planning, scheduling, and quality control.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): This module helps businesses manage their customer relationships, including sales, marketing, and customer service.
Benefits of Using an ERP System
There are many benefits to using an ERP system, including:
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: ERP systems can help streamline business processes, automate tasks, and improve communication. This can lead to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Reduced Costs: ERP systems can help businesses save money by reducing waste, improving inventory management, and streamlining operations.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: ERP systems provide businesses with real-time data and insights, which can help them make better decisions.
- Better Customer Service: ERP systems can help businesses provide better customer service by providing a single view of customer data and by automating tasks such as order processing and customer support.
- Increased Compliance: ERP systems can help businesses meet compliance requirements by providing a centralized platform for managing data and by automating tasks such as reporting.
Conclusion
ERP systems are a powerful tool that can help businesses improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance decision-making. If you are looking for ways to improve your business operations, an ERP system may be a good option for you.
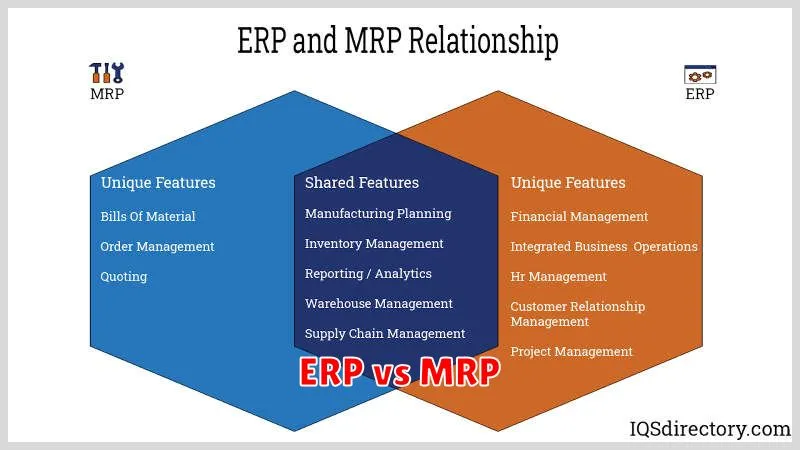
Key Differences Between ERP and MRP
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and MRP (Material Requirements Planning) are two popular business management systems that help organizations manage their resources and processes. While they share some similarities, there are key differences between the two systems that can help you choose the right one for your business.
Scope
The most significant difference between ERP and MRP lies in their scope. MRP is a planning and scheduling system that focuses on managing inventory and production. It helps businesses ensure that they have the right materials in stock at the right time to meet their production needs. On the other hand, ERP is a much broader system that encompasses all aspects of a business, including finance, human resources, sales, marketing, and customer service.
Functionality
MRP’s functionality is primarily focused on inventory and production management. It helps businesses track materials, plan production schedules, and manage inventory levels. ERP, being more comprehensive, offers a wider range of functionalities, including financial accounting, human resource management, supply chain management, customer relationship management (CRM), and business intelligence (BI).
Integration
MRP is typically a standalone system that can be integrated with other systems. ERP, however, is a highly integrated system that consolidates all business data into a single database. This centralized data access allows for greater visibility across the organization, facilitating better decision-making.
Cost
The cost of implementing and maintaining an ERP system is significantly higher than that of an MRP system. This is because ERP involves a larger scope and requires more complex integration and customization. MRP systems, being more focused, tend to be more cost-effective, especially for smaller businesses.
Suitability
MRP is best suited for businesses that need to manage their inventory and production effectively, especially those with a high volume of materials and complex production processes. ERP, with its broader scope and functionalities, is ideal for businesses that need to manage multiple aspects of their operations and gain a comprehensive view of their overall performance.
In Summary
Choosing between ERP and MRP depends on the specific needs of your business. If you need a comprehensive system that integrates all your business processes, ERP is the better choice. However, if your primary focus is on inventory and production management, MRP may be more suitable and cost-effective.
Benefits of MRP for Manufacturers
MRP stands for Material Requirements Planning, a production planning and inventory control system used by manufacturers to manage the production process efficiently. The system helps companies to optimize their production process by ensuring that they have the right materials available at the right time, in the right quantities. This helps manufacturers to meet their customer demands on time and avoid delays in production.
MRP is a powerful tool that can help manufacturers achieve a variety of benefits, including:
Reduced Inventory Costs
One of the main benefits of MRP is that it can help companies to reduce inventory costs. By accurately forecasting demand and planning production, manufacturers can avoid overstocking and holding excess inventory. This can lead to significant savings in storage, handling, and obsolescence costs.
Improved Production Efficiency
MRP can also improve production efficiency by streamlining the production process. By automating tasks such as production planning, scheduling, and material ordering, manufacturers can reduce the amount of time and resources needed to produce goods. This can lead to increased output and lower production costs.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
By ensuring that manufacturers have the materials they need to meet customer demands on time, MRP can enhance customer satisfaction. When customers receive their orders on time and in the correct quantities, they are more likely to be satisfied with the manufacturer’s products and services. This can lead to increased customer loyalty and repeat business.
Better Visibility and Control
MRP provides manufacturers with better visibility and control over their entire production process. The system can track the status of all materials, components, and finished goods, giving manufacturers a clear understanding of what is available and what is needed. This can help them to identify potential bottlenecks and make necessary adjustments to their production plan.
Improved Decision-Making
By providing manufacturers with accurate and timely information about their production process, MRP can improve decision-making. This can help manufacturers to make better decisions about purchasing materials, scheduling production, and allocating resources. This can lead to increased profitability and improved overall performance.
Reduced Lead Times
MRP can also reduce lead times by streamlining the production process. The system helps manufacturers to plan production more efficiently and avoid delays caused by material shortages or production bottlenecks. This can lead to faster delivery times and increased customer satisfaction.
Increased Profitability
By improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing customer satisfaction, MRP can ultimately lead to increased profitability for manufacturers. The system can help manufacturers to maximize their return on investment and achieve their business goals.
Overall, MRP is a valuable tool that can help manufacturers to optimize their production processes, reduce costs, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction. Implementing an MRP system can be a significant investment, but the long-term benefits can be substantial for manufacturers looking to improve their competitiveness and profitability.
Benefits of ERP for Manufacturers
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, companies are constantly looking for ways to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become essential for manufacturers of all sizes, providing a comprehensive solution to manage and streamline operations. This article will explore the key benefits of implementing an ERP system in a manufacturing environment.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
ERP systems automate and integrate critical business processes, eliminating manual tasks and reducing redundancy. With real-time access to data across departments, manufacturers can optimize workflows, eliminate bottlenecks, and streamline production processes. Improved efficiency translates into increased productivity, allowing businesses to achieve more with fewer resources.
Enhanced Inventory Management
ERP systems provide a centralized platform for managing inventory, ensuring accurate tracking of materials, finished goods, and work-in-progress. Real-time inventory visibility enables manufacturers to minimize stockouts, reduce excess inventory, and optimize stock levels. Improved inventory management reduces storage costs, minimizes waste, and ensures timely delivery to customers.
Streamlined Supply Chain Management
ERP systems facilitate seamless communication and collaboration across the supply chain, from raw material suppliers to distributors and customers. Real-time data sharing enables manufacturers to track orders, monitor shipments, and manage supplier relationships effectively. Improved supply chain management reduces lead times, minimizes disruptions, and enhances overall efficiency.
Increased Visibility and Data Insights
ERP systems collect and analyze data from various departments, providing manufacturers with comprehensive insights into their operations. Real-time dashboards and reporting tools offer valuable information about production performance, inventory levels, customer demand, and financial performance. This data-driven approach enables manufacturers to make informed decisions, identify areas for improvement, and optimize resource allocation.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
By streamlining operations and improving efficiency, ERP systems enable manufacturers to meet customer demands more effectively. Enhanced order fulfillment processes, accurate delivery schedules, and improved communication with customers contribute to higher satisfaction levels. By delivering products on time and meeting customer expectations, manufacturers can build strong customer relationships and gain a competitive edge.
Conclusion
Implementing an ERP system can bring significant benefits to manufacturers, including improved efficiency, enhanced inventory management, streamlined supply chain, increased visibility, and improved customer satisfaction. By leveraging the power of ERP, manufacturers can optimize their operations, reduce costs, and achieve sustainable growth in today’s competitive market.
When to Choose MRP vs. ERP
Choosing between MRP and ERP systems can be a challenging decision for businesses, especially if you’re unsure of the distinctions between the two and their respective benefits. Both systems aim to streamline processes and improve efficiency, but they focus on different aspects of a business. This article will break down the key differences between MRP and ERP to help you determine which system is right for your organization.
What is MRP?
MRP, or Material Requirements Planning, is a software system designed primarily for managing inventory and production. It uses a bill of materials (BOM) to calculate the raw materials needed for each product and then creates a schedule for procuring and assembling these materials. MRP focuses on optimizing production processes by minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency. It is particularly beneficial for manufacturing companies that require precise planning and tracking of inventory levels.
What is ERP?
ERP, or Enterprise Resource Planning, is a broader and more comprehensive system that manages various aspects of a business, including finance, human resources, and customer relationship management (CRM), in addition to manufacturing and inventory. ERP integrates all these departments into a single platform, allowing for seamless data sharing and communication across the organization. This integration leads to better visibility, improved decision-making, and reduced errors. Unlike MRP, ERP is not just for manufacturers; it can benefit businesses in diverse industries, from retail to services.
When to Choose MRP
Consider choosing an MRP system if your business:
- Focuses primarily on manufacturing operations
- Requires precise inventory control and production planning
- Has a limited budget and needs a solution specifically tailored for manufacturing
When to Choose ERP
Consider choosing an ERP system if your business:
- Operates across multiple departments and needs a unified platform for managing them
- Requires real-time data visibility and reporting for informed decision-making
- Seeks to improve overall business efficiency and optimize processes across the entire organization
Conclusion
The best choice between MRP and ERP depends on your business’s specific needs and goals. If your focus is primarily on manufacturing and inventory management, an MRP system might be sufficient. However, if you require a comprehensive platform for managing your entire business, ERP is the better option. Carefully consider your business processes, budget, and future growth plans before making a decision. Consulting with industry experts can also provide valuable insights and help you make an informed choice.
Integration of ERP and MRP Systems
The integration of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Material Requirements Planning (MRP) systems has become increasingly critical for organizations seeking to optimize their operations and gain a competitive advantage. By integrating these systems, businesses can streamline their processes, reduce costs, and enhance efficiency across various departments.
Benefits of ERP and MRP Integration
The integration of ERP and MRP systems offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Inventory Management: Real-time visibility into inventory levels and demand forecasts allows for accurate stock management, reducing inventory holding costs and stockouts.
- Enhanced Production Planning: By integrating production data with demand forecasts, businesses can optimize production schedules, minimize delays, and improve on-time delivery.
- Streamlined Supply Chain: Integration enables better communication and collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, leading to a more efficient supply chain.
- Reduced Costs: Optimized inventory management, improved production planning, and streamlined supply chains result in reduced costs associated with excess inventory, production delays, and supply chain disruptions.
- Increased Efficiency: By automating tasks and providing real-time data, integrated systems enhance operational efficiency and productivity.
Key Considerations for Integration
While integrating ERP and MRP systems offers significant benefits, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
- Business Requirements: Define specific business objectives and processes that need to be integrated.
- Data Synchronization: Ensure seamless data exchange and synchronization between the two systems.
- System Compatibility: Choose systems that are compatible and can effectively integrate with each other.
- Implementation Strategy: Develop a comprehensive implementation plan with clear timelines, resources, and communication strategies.
- Training and Support: Provide adequate training to users and ensure ongoing support for the integrated system.
Conclusion
Integrating ERP and MRP systems is a strategic investment that can significantly enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve supply chain management. By carefully considering the benefits, key considerations, and implementation steps, businesses can reap the full potential of integrated systems and gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic market.
Case Studies of MRP and ERP in Manufacturing

In the dynamic and competitive landscape of manufacturing, organizations are constantly seeking ways to enhance efficiency, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall productivity. Two prominent tools that have revolutionized manufacturing operations are Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. This article delves into case studies of MRP and ERP implementation in various manufacturing sectors, highlighting their benefits and challenges.
Case Study 1: Automotive Industry
A leading automotive manufacturer, facing challenges in managing complex supply chains and maintaining accurate inventory levels, implemented an MRP system. The system enabled them to forecast demand accurately, plan production schedules effectively, and minimize stockouts. By automating purchase orders and tracking material flow, the manufacturer significantly reduced lead times, optimized inventory costs, and improved overall production efficiency. This resulted in enhanced customer satisfaction and increased market competitiveness.
Case Study 2: Electronics Manufacturing
An electronics manufacturer, struggling with fragmented data and manual processes, adopted an ERP system. The ERP system integrated all core business functions, including finance, production, inventory, and sales. This centralized platform provided real-time visibility into operations, streamlined workflows, and eliminated redundant tasks. The manufacturer experienced improved financial transparency, reduced operational costs, and enhanced decision-making capabilities.
Case Study 3: Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
A pharmaceutical company, operating in a highly regulated industry, implemented an ERP system that complied with industry standards. The ERP system facilitated compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other regulatory requirements. It also provided a secure platform for managing sensitive patient data and ensuring product traceability. This resulted in improved quality control, reduced risk of non-compliance, and enhanced patient safety.
Challenges and Considerations
While MRP and ERP systems offer significant benefits, their implementation can present challenges. Change management is crucial, as employees need to adapt to new processes and workflows. Data migration can be complex, requiring thorough planning and execution. Integration with existing systems may also pose difficulties. Furthermore, ongoing support and maintenance are essential to ensure the systems remain up-to-date and effective.
Conclusion
Case studies demonstrate the transformative impact of MRP and ERP systems in manufacturing. These systems enable organizations to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. By addressing challenges effectively and leveraging their capabilities, manufacturers can achieve significant operational improvements and drive business growth.