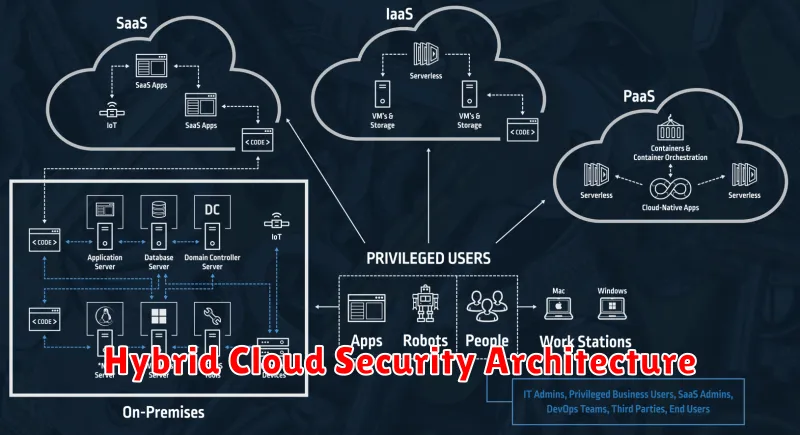
The hybrid cloud is becoming increasingly popular, offering businesses the flexibility and scalability of public cloud services while maintaining the control and security of on-premises infrastructure. However, this combination also introduces new security challenges. With an increasing attack surface, it’s more important than ever to adopt best practices for server security in hybrid cloud environments. This guide will help you understand the key aspects of securing your servers in this complex environment, from network segmentation and data encryption to identity and access management and vulnerability scanning.
Understanding Hybrid Cloud Environments
In today’s digital world, organizations are increasingly turning to cloud computing to meet their ever-growing IT needs. While public cloud providers offer a wide range of services and scalability, many organizations also have on-premises infrastructure that they need to integrate and manage. This is where hybrid cloud environments come into play.
A hybrid cloud environment is a combination of on-premises infrastructure and public cloud services. This allows organizations to leverage the best of both worlds, taking advantage of the flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness of the public cloud while maintaining control over their critical data and applications on-premises.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
There are several benefits to adopting a hybrid cloud strategy, including:
- Improved Flexibility and Scalability: Organizations can easily scale their resources up or down based on demand, leveraging the public cloud for peak workloads and keeping critical applications on-premises for stability.
- Cost Optimization: By shifting less critical workloads to the public cloud, organizations can reduce their on-premises hardware and software costs.
- Enhanced Security: Sensitive data and applications can be kept on-premises while leveraging the robust security features of public cloud providers for less critical workloads.
- Increased Agility: Hybrid cloud allows organizations to quickly deploy new applications and services, improving their overall agility and competitiveness.
Key Components of a Hybrid Cloud Environment
A hybrid cloud environment typically consists of the following components:
- On-premises infrastructure: This includes servers, storage, networking equipment, and other hardware and software resources that are physically located within an organization’s data center.
- Public cloud services: These are services provided by third-party cloud providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These services can include computing, storage, networking, databases, and more.
- Connectivity: A secure and reliable connection is needed between the on-premises infrastructure and the public cloud services to ensure seamless communication and data transfer.
- Management tools: Organizations need tools to manage their hybrid cloud environment effectively, including monitoring, security, and orchestration capabilities.
Challenges of Hybrid Cloud
While hybrid cloud offers numerous benefits, there are also challenges that organizations need to address:
- Complexity: Managing a hybrid cloud environment can be complex, requiring expertise in both on-premises and cloud technologies.
- Security: Ensuring data security across both on-premises and public cloud environments requires careful planning and implementation.
- Integration: Integrating on-premises infrastructure with public cloud services can be challenging, especially for legacy systems.
Conclusion
Hybrid cloud environments provide organizations with a flexible and scalable way to meet their IT needs while leveraging the best of both on-premises and public cloud solutions. By carefully planning and managing their hybrid cloud infrastructure, organizations can reap the numerous benefits of this approach and gain a competitive edge in the digital world.
Security Challenges in Hybrid Cloud
The adoption of hybrid cloud architectures has grown rapidly in recent years, as organizations seek to balance the benefits of public cloud with the need for on-premises control. However, this approach also introduces new and complex security challenges that must be addressed to ensure the protection of sensitive data and applications.
Data Security and Privacy
One of the primary concerns in hybrid cloud environments is data security and privacy. Data may be stored in multiple locations, including on-premises servers, public cloud providers, and even third-party applications. This distributed data landscape makes it challenging to maintain consistent security policies and controls. Furthermore, the use of public cloud services can introduce risks associated with data breaches, especially if proper security measures are not in place.
Network Security
Hybrid cloud environments often involve complex network configurations, with data flowing between on-premises and public cloud infrastructure. This can create vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malicious actors. For example, insufficient network segmentation or improper configuration of firewalls can expose sensitive data to unauthorized access. Securely connecting on-premises and cloud environments is crucial to prevent data leakage and maintain overall security.
Identity and Access Management
Managing identities and access privileges across multiple environments in a hybrid cloud can be a complex and challenging task. Inconsistent access control policies and the use of multiple identity providers can create security gaps. Organizations must establish a centralized identity and access management (IAM) system that provides consistent authentication and authorization across all hybrid cloud components.
Compliance and Governance
Meeting compliance requirements can be more difficult in hybrid cloud environments. Different regulations may apply to on-premises and cloud resources, and organizations must ensure that their security controls meet all applicable standards. Implementing strong governance practices, including regular security audits and vulnerability assessments, is essential for maintaining compliance and mitigating risks.
Security Monitoring and Incident Response
Effective security monitoring is essential for detecting and responding to threats in hybrid cloud environments. Organizations need to implement comprehensive logging and monitoring solutions that cover both on-premises and cloud resources. Additionally, they should have a well-defined incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in case of a security breach.
Conclusion
While hybrid cloud architectures offer significant advantages, organizations must be aware of the inherent security challenges. By implementing robust security controls, adopting best practices, and staying vigilant against emerging threats, businesses can effectively mitigate risks and secure their hybrid cloud environments.
Implementing Strong Access Control Policies
Strong access control policies are essential for securing any system, whether it’s a personal computer, a corporate network, or a cloud-based application. These policies are designed to limit access to sensitive information and resources only to authorized users, preventing unauthorized access, modification, or deletion. Implementing robust access control policies involves a comprehensive approach that encompasses various aspects, from defining clear access rules to enforcing them with appropriate tools and technologies.
Defining Access Control Policies
The first step in implementing strong access control policies is to clearly define what access is allowed and what is prohibited. This requires identifying the different types of users, their roles, and the resources they need access to. For example, a company might have employees, contractors, and customers, each with different access levels. Employees might have access to internal systems and data, while contractors might only have access to specific projects. Defining these roles and permissions helps establish a baseline for access control.
Implementing Access Control Mechanisms
Once the access control policies are defined, it’s necessary to implement mechanisms to enforce them. These mechanisms can include:
- Authentication: Verifying the identity of users before granting access. This can be achieved through various methods like passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication.
- Authorization: Determining what resources a user has access to based on their role and permissions. This involves assigning access rights to specific resources or data.
- Auditing: Tracking user activity and access attempts to identify potential security breaches or unauthorized access. This helps monitor access control policies and detect any violations.
- Least Privilege: Granting users only the access they need to perform their job functions. This principle minimizes the impact of potential security breaches, as users with limited access cannot cause as much damage.
Using Technology for Access Control
Various technologies are available to assist in implementing and enforcing access control policies:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) Systems: These centralized systems manage user identities and access rights across multiple applications and systems. They provide a comprehensive platform for defining and enforcing access control policies.
- Firewall: These network security devices act as a barrier between the internal network and external threats. They block unauthorized access to the network and control traffic flow.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can block or alert about potential security threats.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools: These tools identify and prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s network. They help protect against data breaches and unauthorized data sharing.
Continuously Monitoring and Updating Access Control Policies
Implementing strong access control policies is an ongoing process that requires constant monitoring and updating. As the organization’s needs and the threat landscape evolve, access control policies must adapt to remain effective. Regular security audits, vulnerability assessments, and user behavior analysis can help identify areas for improvement and ensure that access control policies remain robust and up-to-date.
Data Encryption at Rest and in Transit

Data encryption is a crucial security measure that protects sensitive information from unauthorized access. It involves transforming data into an unreadable format, making it incomprehensible to anyone without the proper decryption key. Data encryption can be implemented in two primary ways: at rest and in transit.
Data Encryption at Rest
Data encryption at rest refers to protecting data while it is stored on physical devices, such as hard drives, servers, or cloud storage. This involves encrypting the data before it is written to the storage medium. Even if the device is physically compromised, the encrypted data will remain inaccessible without the decryption key.
Common methods for data encryption at rest include:
- Full disk encryption (FDE): Encrypts the entire hard drive, ensuring that all data is protected.
- File-level encryption: Encrypts individual files or folders, allowing selective protection of specific data.
- Database encryption: Encrypts data within databases, safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Data Encryption in Transit
Data encryption in transit protects data while it is being transmitted across networks, such as the internet or local area networks. This involves encrypting the data before it is sent and decrypting it upon arrival at the destination. This prevents eavesdropping and interception of sensitive information during transmission.
Common methods for data encryption in transit include:
- Transport Layer Security (TLS): A protocol that encrypts communication between web browsers and servers, ensuring secure data exchange over the internet.
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL): An older protocol similar to TLS, which is also commonly used for secure web communication.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): Creates a secure tunnel for data transmission over public networks, encrypting all traffic passing through it.
Importance of Data Encryption
Data encryption is essential for safeguarding sensitive information and complying with data protection regulations. It helps mitigate the risks of data breaches, identity theft, and financial loss. By encrypting data, organizations can ensure that even if unauthorized individuals gain access to the data, they will be unable to read or understand it.
Conclusion
Data encryption at rest and in transit is fundamental to maintaining data security. Implementing robust encryption measures is crucial for protecting sensitive information and preventing unauthorized access. Organizations should prioritize data encryption as a core security practice to safeguard their data assets and comply with regulatory requirements.
Network Security Best Practices for Hybrid Cloud

In today’s digital landscape, businesses are increasingly adopting hybrid cloud strategies to leverage the benefits of both on-premises and cloud environments. While hybrid cloud offers flexibility and scalability, it also presents unique challenges for network security. To ensure the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive data, it’s crucial to implement robust security best practices. This article will delve into some essential considerations for securing your hybrid cloud environment.
1. Segment Your Network
Network segmentation is a fundamental security principle that involves dividing your network into smaller, isolated segments. This approach limits the impact of potential security breaches by preventing attackers from accessing sensitive data across different parts of your network. In a hybrid cloud setup, it’s essential to segment your on-premises network from your cloud infrastructure and further subdivide each environment based on their security requirements.
2. Implement Strong Access Controls
Strong access controls are paramount to prevent unauthorized access to your hybrid cloud resources. Utilize a combination of technologies, including multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access control (RBAC), and strong password policies, to enforce granular access permissions. By limiting access based on user roles and privileges, you can minimize the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
3. Secure Your Data at Rest and in Transit
Data security encompasses protecting data both at rest and in transit. Encryption is a critical tool for achieving this goal. Encrypt data at rest using technologies like disk encryption or data encryption at rest services offered by cloud providers. For data in transit, utilize secure communication protocols like HTTPS, TLS/SSL, and VPNs to prevent eavesdropping and data interception.
4. Utilize Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
A SIEM solution provides a centralized platform for collecting, analyzing, and correlating security events across your hybrid cloud environment. By aggregating logs from various sources, including on-premises servers, cloud services, and network devices, SIEM enables you to detect anomalies, identify potential threats, and respond promptly to security incidents.
5. Implement Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Scanning
Proactive security measures are essential to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities before they are exploited. Conduct regular security audits to assess your security posture and identify any weaknesses. Implement automated vulnerability scanning tools to detect and remediate vulnerabilities in your infrastructure, applications, and operating systems.
6. Stay Informed and Adapt to Evolving Threats
The threat landscape is constantly evolving, so staying informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities is critical. Subscribe to security industry newsletters, attend webinars, and engage with cybersecurity communities to stay abreast of the latest security trends and best practices. Continuously assess and adapt your security posture to address new threats and vulnerabilities.
By implementing these network security best practices, you can create a more secure hybrid cloud environment that protects your sensitive data and minimizes the risk of cyberattacks. Remember that security is an ongoing process, and you must continuously adapt your strategies to address the ever-changing threat landscape.
Regular Security Audits and Monitoring
Regular security audits and monitoring are crucial for any organization that wants to protect its data and systems from cyber threats. Security audits are a comprehensive review of an organization’s security posture, while monitoring provides real-time insights into potential vulnerabilities and attacks.
Benefits of Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits offer numerous benefits, including:
- Identification of vulnerabilities: Audits help identify weaknesses in an organization’s security controls that could be exploited by attackers.
- Compliance with regulations: Many industries have specific security standards and regulations that organizations must comply with. Audits ensure compliance and minimize the risk of penalties.
- Improved security posture: By identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, organizations can strengthen their security posture and reduce the risk of breaches.
- Peace of mind: Knowing that your organization’s security is regularly reviewed can provide peace of mind and confidence in your data protection practices.
Types of Security Audits
There are several types of security audits, each focusing on different aspects of an organization’s security posture. Common types include:
- Vulnerability assessments: These audits identify potential vulnerabilities in systems, applications, and networks.
- Penetration testing: This type of audit simulates a real-world attack to identify weaknesses in an organization’s security defenses.
- Compliance audits: These audits verify compliance with industry standards and regulations, such as PCI DSS or HIPAA.
- Risk assessments: These audits identify and evaluate potential security risks and their impact on the organization.
Importance of Security Monitoring
Security monitoring is essential for detecting and responding to security incidents in real-time. Effective monitoring systems provide:
- Real-time threat detection: Monitoring tools can identify suspicious activity and potential threats, alerting security teams to potential breaches.
- Early incident response: By detecting incidents early, organizations can respond quickly and minimize the impact of attacks.
- Continuous security improvement: Monitoring data provides valuable insights into security trends and helps organizations continuously improve their security practices.
Best Practices for Security Audits and Monitoring
To maximize the benefits of security audits and monitoring, consider these best practices:
- Regular audits: Conduct audits regularly, at least annually, and more frequently for critical systems.
- Independent audits: Engage independent security experts to conduct audits to ensure objectivity and thoroughness.
- Comprehensive monitoring: Implement a comprehensive monitoring solution that covers all critical systems, applications, and networks.
- Automated alerts: Configure automated alerts for suspicious activity and potential security threats.
- Continuous improvement: Regularly review audit findings and monitoring data to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments.
By prioritizing regular security audits and monitoring, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of cyber attacks and protect their valuable data and systems.
Vulnerability Management and Patching
Vulnerability management is the process of identifying, assessing, prioritizing, and mitigating vulnerabilities in systems and applications. This includes identifying and addressing weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access, steal data, or disrupt operations.
Patching is a critical aspect of vulnerability management. Patches are software updates that fix known vulnerabilities. Applying patches promptly is essential for preventing exploitation of vulnerabilities and reducing the risk of security incidents.
Key Components of Vulnerability Management
A comprehensive vulnerability management program typically includes the following components:
- Vulnerability Scanning: Regularly scanning systems and applications for known vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Analyzing identified vulnerabilities to determine their severity and potential impact.
- Patch Management: Implementing a process for deploying patches to fix vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Remediation: Taking steps to address vulnerabilities that cannot be patched, such as through configuration changes or workarounds.
- Reporting and Tracking: Monitoring vulnerability status and reporting on progress made in mitigating vulnerabilities.
Benefits of Vulnerability Management and Patching
Effective vulnerability management and patching offer numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced Risk of Security Incidents: By addressing vulnerabilities promptly, organizations can minimize the likelihood of successful attacks.
- Improved Security Posture: A strong vulnerability management program strengthens overall security posture.
- Enhanced Compliance: Many regulatory frameworks require organizations to implement effective vulnerability management practices.
- Cost Savings: Proactive vulnerability management can help prevent costly security breaches and downtime.
Best Practices for Vulnerability Management and Patching
To ensure effective vulnerability management and patching, organizations should follow these best practices:
- Implement a Formal Vulnerability Management Program: Document policies and procedures for identifying, assessing, and mitigating vulnerabilities.
- Use Automated Tools: Utilize vulnerability scanning tools and patch management solutions to streamline processes.
- Prioritize Vulnerabilities: Focus on addressing the most critical vulnerabilities first.
- Regularly Patch Systems: Develop a schedule for applying patches and ensure that patches are tested before deployment.
- Educate Employees: Train employees on the importance of vulnerability management and how to report potential vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Vulnerability management and patching are essential components of any comprehensive security strategy. By implementing effective practices and leveraging appropriate tools, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of security incidents and enhance their overall security posture.
Incident Response Planning and Testing
Incident response planning is a critical aspect of cybersecurity that involves defining and documenting procedures for responding to security incidents. It is a proactive approach to mitigating potential damage and ensuring business continuity in the event of a breach. An effective incident response plan outlines the steps to be taken, the roles and responsibilities of team members, and the communication channels to be used. The plan should be regularly tested and updated to reflect changing threats and vulnerabilities.
The first step in incident response planning is to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities. This can be done through a comprehensive risk assessment, considering factors such as industry trends, threat actor tactics, and internal weaknesses. Once potential threats are identified, it is important to understand their impact and likelihood of occurrence. Based on this analysis, organizations can prioritize their efforts and allocate resources accordingly.
The next step is to develop a clear incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident. This plan should include the following key components:
- Incident Detection and Reporting: Defining procedures for detecting and reporting incidents, including the use of security monitoring tools, alert mechanisms, and escalation procedures.
- Incident Containment: Establishing measures to isolate the affected system or network to prevent further damage or spread of the incident.
- Incident Eradication: Describing steps to remove the root cause of the incident and restore affected systems to a secure state.
- Recovery and Lessons Learned: Implementing procedures for restoring systems to their normal operating state and analyzing the incident to identify weaknesses and improve future response efforts.
- Communication and Reporting: Defining communication channels for internal and external stakeholders, including incident reporting, updates, and post-incident summaries.
Once the plan is developed, it is essential to test it regularly to ensure its effectiveness. Simulated attack scenarios, known as tabletop exercises, can be used to assess the team’s response capabilities, identify gaps in the plan, and refine procedures. Regular testing helps to ensure that the plan is up-to-date, relevant, and adaptable to changing threats.
Incident response planning is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement and adaptation. As new threats emerge and technologies evolve, organizations must update their plans to reflect the latest best practices. By investing in robust incident response planning and testing, organizations can enhance their resilience to cyberattacks, minimize potential damage, and protect their critical assets.
Choosing the Right Security Tools
In today’s digital landscape, security is paramount. With cyber threats constantly evolving, it’s more important than ever to have the right security tools in place to protect your organization. But with so many options available, choosing the right tools can be a daunting task. This guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview of essential security tools, helping you make informed decisions to safeguard your assets.
Understanding Your Needs
Before you start researching security tools, it’s crucial to understand your specific needs. Consider the following factors:
- Size and type of your organization: A small business will have different security needs than a large enterprise.
- Industry: Certain industries are more susceptible to specific types of attacks.
- Data sensitivity: The level of sensitivity of your data will determine the level of security required.
- Budget: Security tools can range in price, so it’s essential to consider your budget constraints.
Essential Security Tools
Here are some of the essential security tools that every organization should consider:
1. Antivirus and Anti-malware
Antivirus and anti-malware software are crucial for protecting your devices from malware, viruses, and other threats. They scan your system for malicious software and prevent it from harming your data.
2. Firewall
A firewall acts as a barrier between your network and the outside world, blocking unauthorized access to your systems. It can be implemented as a hardware device or software solution.
3. Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS)
IDS/IPS systems monitor your network for suspicious activity and can block or alert you to potential threats. They help detect and prevent attacks in real-time.
4. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
DLP solutions help prevent sensitive data from leaving your organization without authorization. They can monitor network traffic and data transfers to identify and block unauthorized data leaks.
5. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
SIEM systems collect and analyze security data from various sources, providing a comprehensive view of your security posture. They help detect anomalies, correlate events, and provide valuable insights into security threats.
6. Security Awareness Training
Security awareness training is essential for educating your employees about common cyber threats and best practices for protecting themselves and your organization. It helps prevent human error and reduce the risk of phishing attacks and other social engineering techniques.
Choosing the Right Tools for You
Once you’ve identified your needs, you can start researching and comparing different security tools. Consider the following factors:
- Features: Make sure the tool offers the features you need to protect your organization.
- Ease of use: Choose a tool that is easy to manage and deploy.
- Integration: Look for tools that can integrate with your existing systems and workflows.
- Support: Choose a vendor that provides excellent customer support.
Conclusion
Choosing the right security tools is essential for protecting your organization from cyber threats. By understanding your needs and considering the key factors outlined in this guide, you can make informed decisions and build a robust security infrastructure. Remember, security is an ongoing process, so it’s important to regularly review and update your security tools and strategies to stay ahead of evolving threats.